Intermittent and fluctuating output
Severe impact on the stability of the power grid.
World-leading state owned corporation in the manufacturing of electric utility systems with 125 years of history
Shanghai Electric Group is a global leader in the manufacture and EPC of innovative utility-scale energy systems, focusing on three business areas: the production of systems for energy generation, energy distribution, and energy storage, in order to offer its customers innovative, sustainable, and reliable complete solutions.
Shanghai Electric’s many years of experience and know-how in conventional power plant construction, renewable energy systems, power transmission, as an EPC contractor, and the manufacturing of all necessary products create comprehensive competitive advantages for the development, manufacturing, installation, and operation of energy storage systems (BESS and ESS). The company can offer “innovative” storage system solutions, switchgear, transformer stations, and a complete EPC service including O&M from a single source for energy producers, grid operators, electricity traders, and for industry.
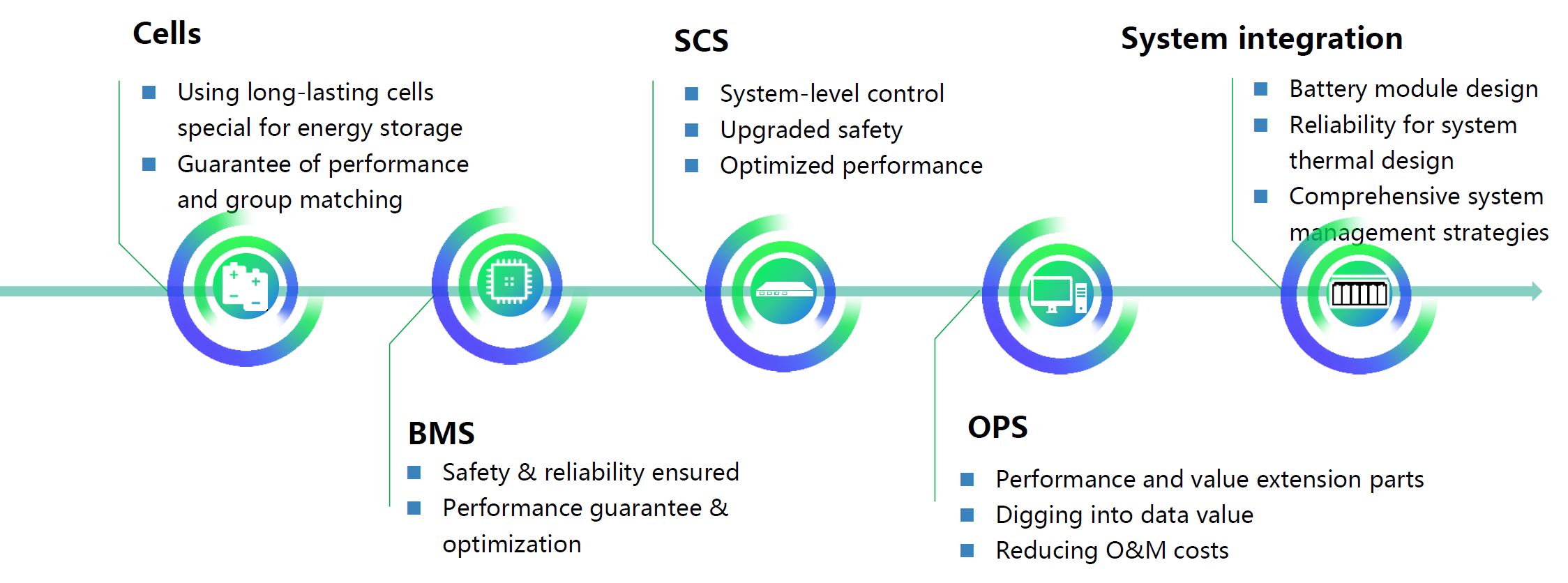
The most important success factors of the turnkey BESS and ESS solutions from Shanghai Electric for our customers
Shanghai Electric is not only a long-standing experienced manufacturer of BESS battery systems, but also a comprehensive system integrator (EPC) of innovative power storage solutions for national and regional electricity utility companies. The company’s KNOW-HOW and industrial experience guarantee customers innovative and proven total solutions for energy producers, grid operators, power traders, and industry.
Unleash the full potential of your renewable energy systems or conventional power plants with Shanghai Electric’s advanced battery storage solutions. Experience unmatched flexibility, efficiency, and reliability with our comprehensive BESS solutions tailored to your individual needs. Don’t miss the opportunity to revolutionize your energy storage and take a step towards a greener, more sustainable future with us.
Revolutionize your energy storage with Shanghai Electric’s BESS solutions. Increase your system capacities and flexibility and improve system behavior for renewable energies with Shanghai Electric’s groundbreaking battery energy storage solutions (BESS). As a proven, experienced, and trusted partner in the energy industry and renewable energy large projects, we are here to provide you with the most advanced and reliable BESS solutions tailored to your unique needs. Whether you are a renewable plant owner, power plant operator, grid operator, project developer, or investor, our flexible and comprehensive approach ensures that you benefit from the best and most reliable available energy storage technology.
Continuously enhance and ensure the development of the energy storage field with high levels of safety, efficiency, lifespan and intellectualization.
Shanghai Electric is a BESS battery provider and a large, full-scale utility energy system manufacturer & integrator. They provide total solutions for energy generation, state-of-the-art grid systems with smart transmission lines and high quality energy storage and O&M solutions to final consumers.
ILB Helios Holding AG is an official representative of Shanghai Electric and provides with key-partners complied turnkey solutions including the design, EPC, grid connection, operation & maintenance, monitoring systems, investment solutions, leasing possibilities, insurance packages including energy trading.
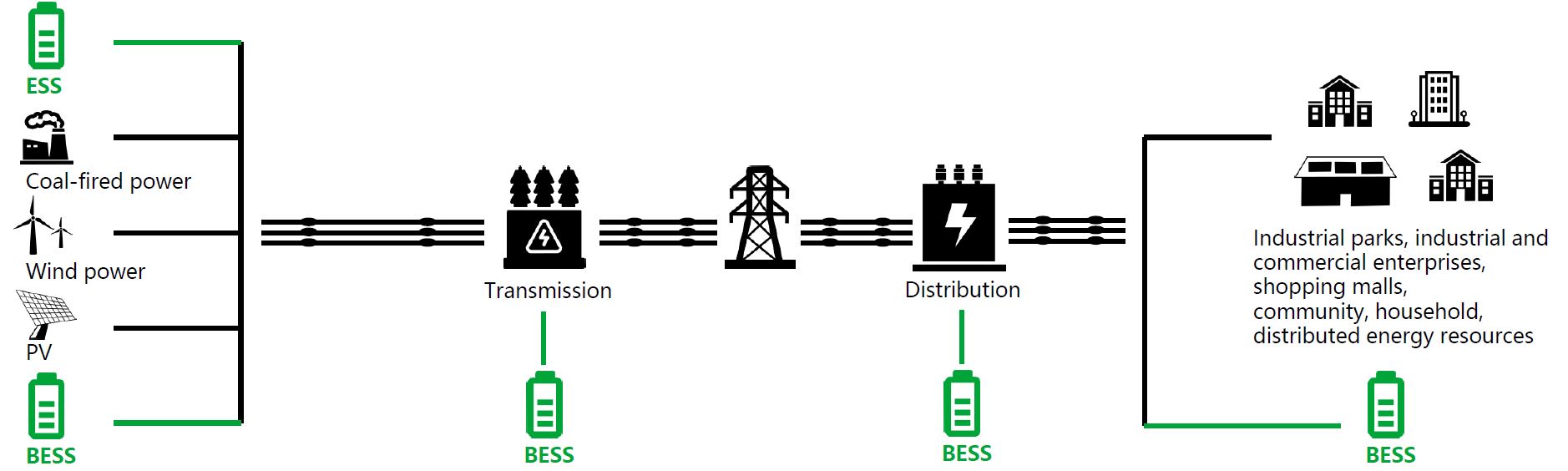
Power generation
Power transmission
Power distribution
User Side
Severe impact on the stability of the power grid.
Wind and PV curtailment, electricity shortage
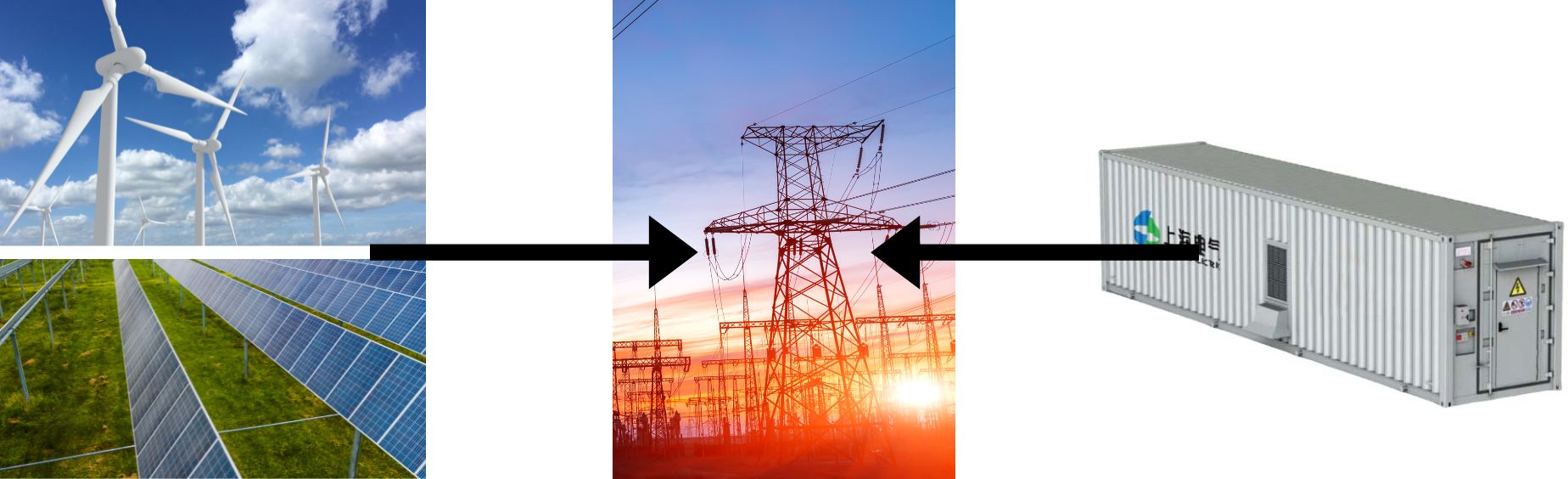

Continuous and stable output
Planned grid dispatching
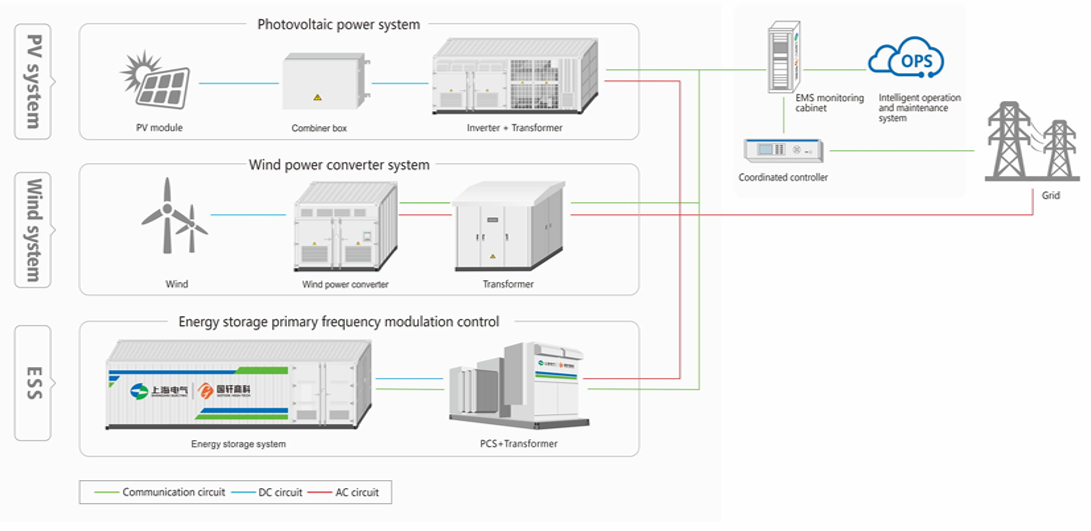













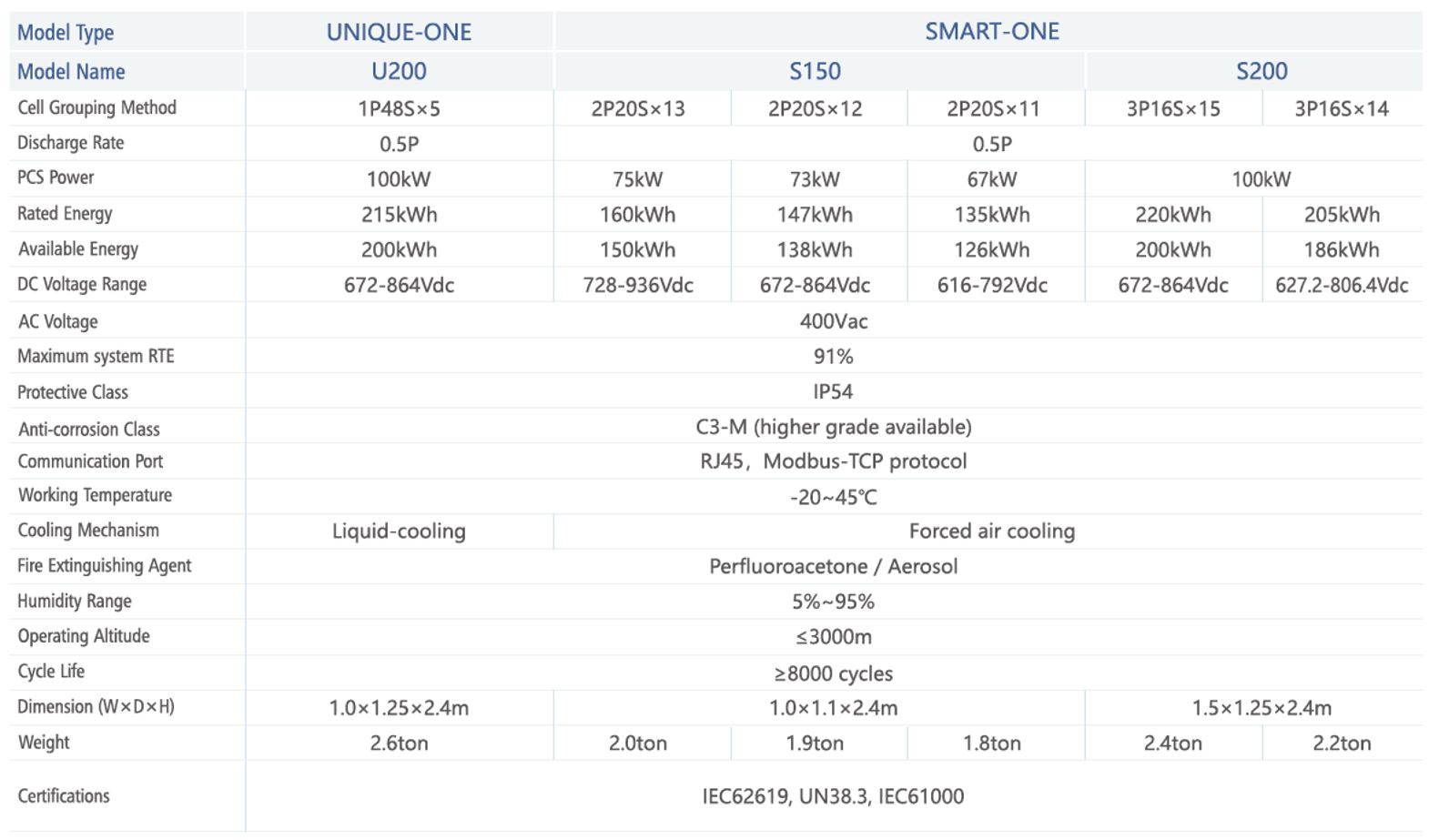
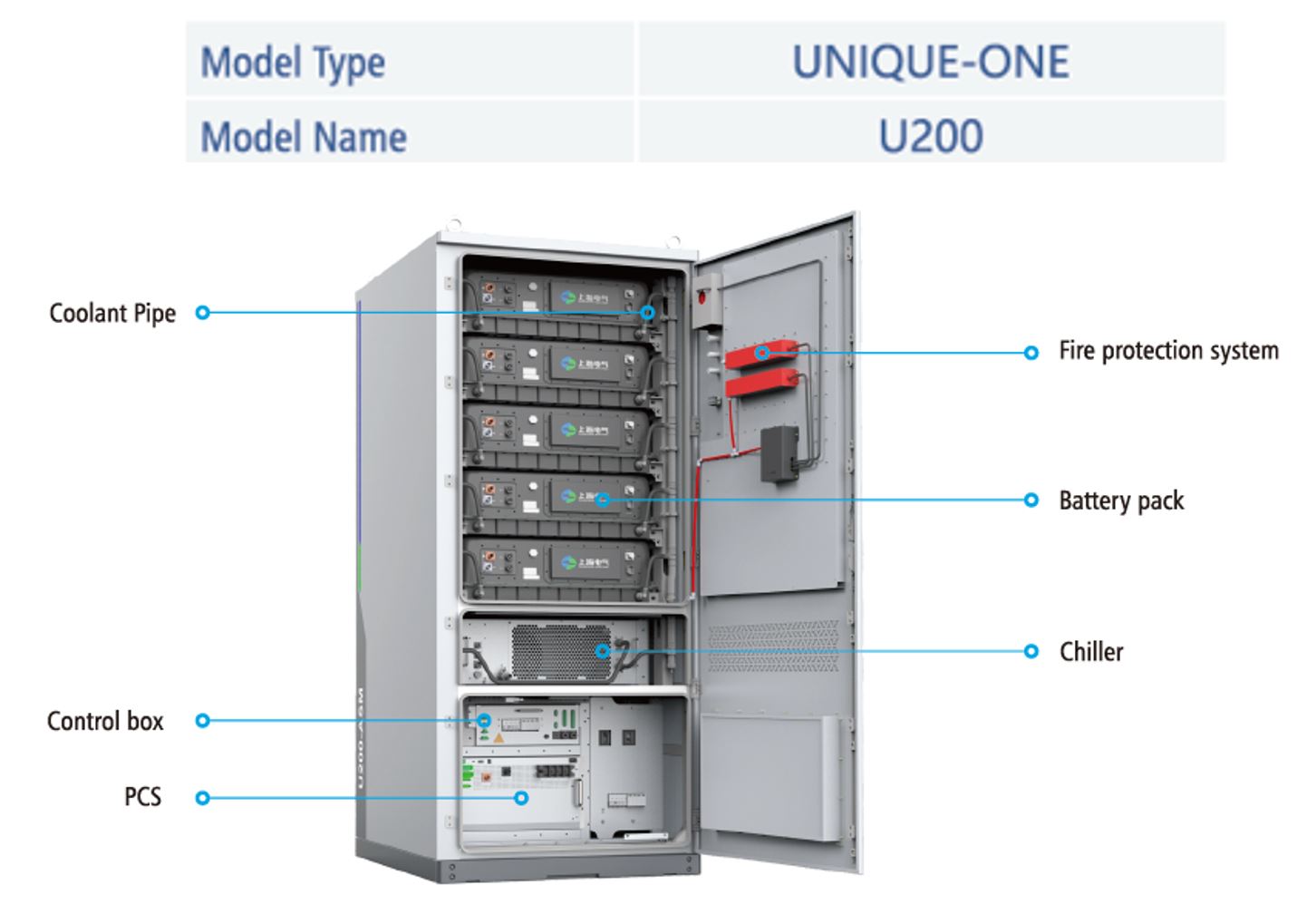
SMART-ONE and UNIQUE-ONE C&I ESS products are made by Shanghai Electric Gotion for industrial and commercial application scenarios, aimed to provide a solution with high-safety, high-reliability and easy scalability. These products adopt a highly integrated system design and can flexibly match various C&I scenarios. They can help relieve grid pressure through the practice of peak-shaving / energy shifting under different electricity consumption patterns. It is also suitable for applications in microgrid scenarios.
The products are divided into two types: SMART-ONE and UNIQUE-ONE. The SMART-ONE product is easy to operate and maintain and can be flexibly configured in capacity; the UNIQUE-ONE product is more compact and has a high energy density.
(*if allowed by local law & regulations)

zero-carbon industrial parks

solar-storage-charging stations

CBD centers

Data centers

5G stations

house-hold

micro-grid

mining area

power backup

city railways
F400 C&l ESS product is made by Shanghai Electric for industrial and commercial application scenarios, aiming to provide a solution with high safety, high reliability, and easy scalability. The product adopts a highly integrated system design and it can flexibly match various C&l scenarios. The product can help relieve grid pressure through the practice of peak shaving or energy shifting under different electricity consumption patterns, and it is suitable for applications in micro grid scenarios. The product is also equipped with Smart OPS which can help achieve real time monitoring and remote control.
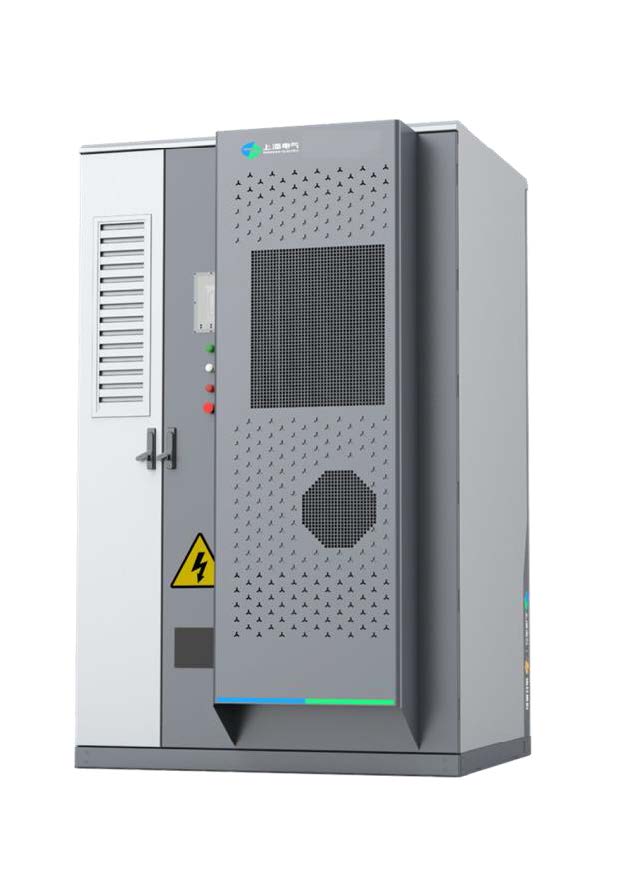

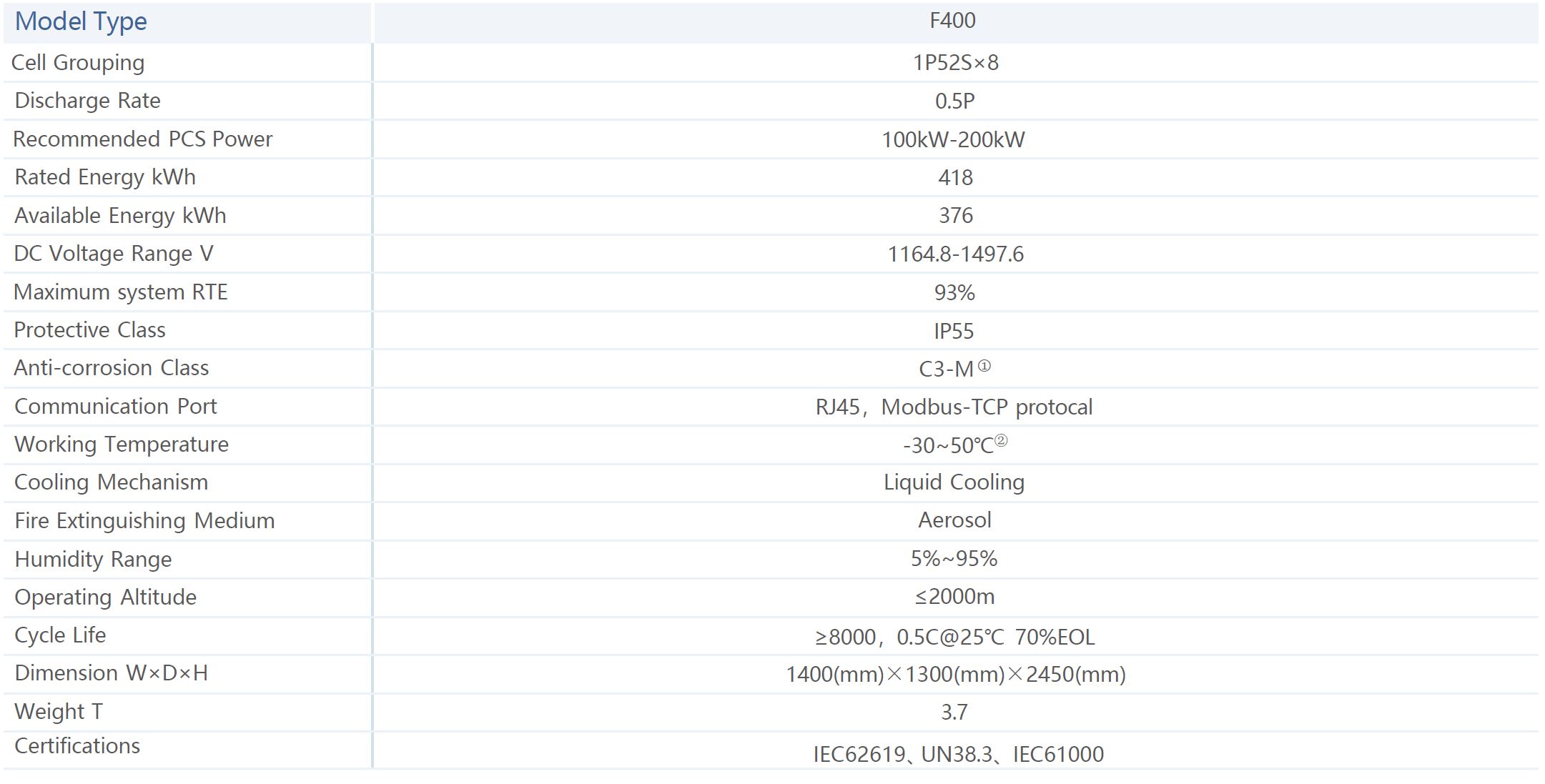
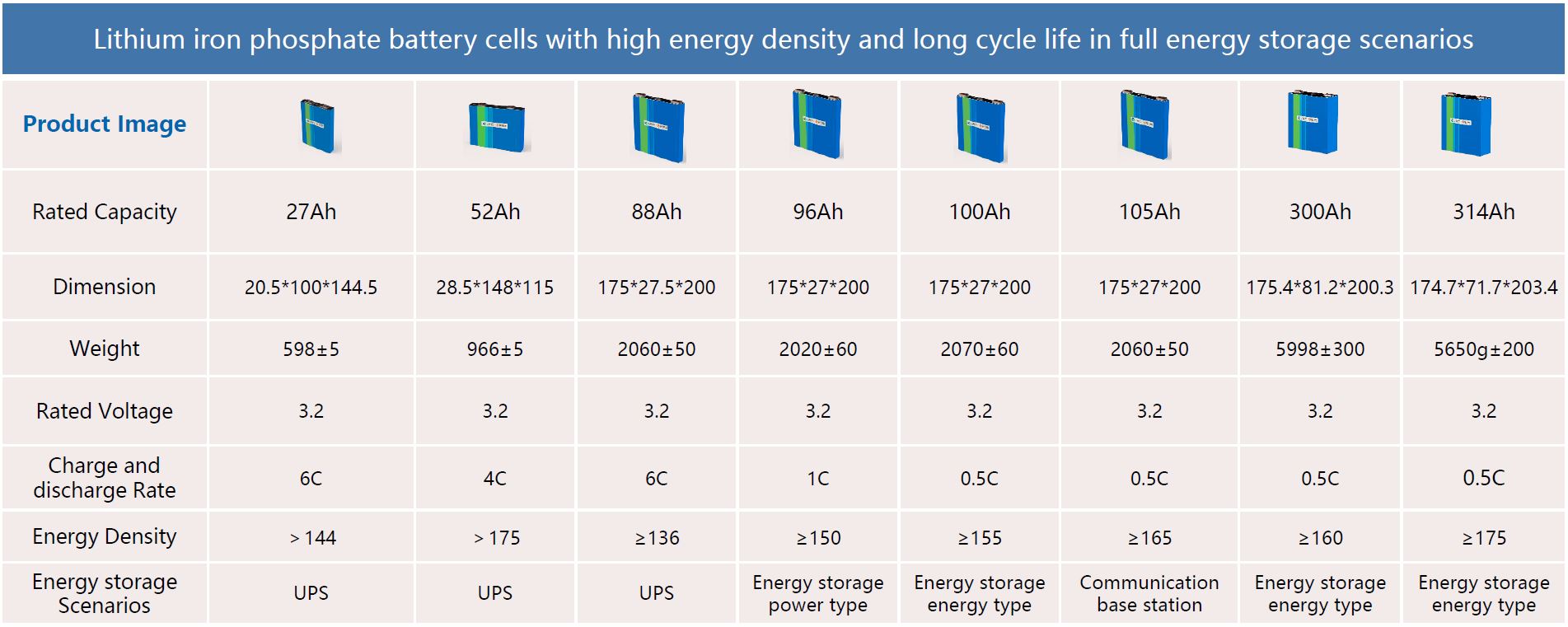
Note: The product picture is for reference ONLY.
Note ①:The standard anti corrosion class is C3-M , while a higher class can be customizable.
Note ②:Usage over 45℃ working temperature will be derating.
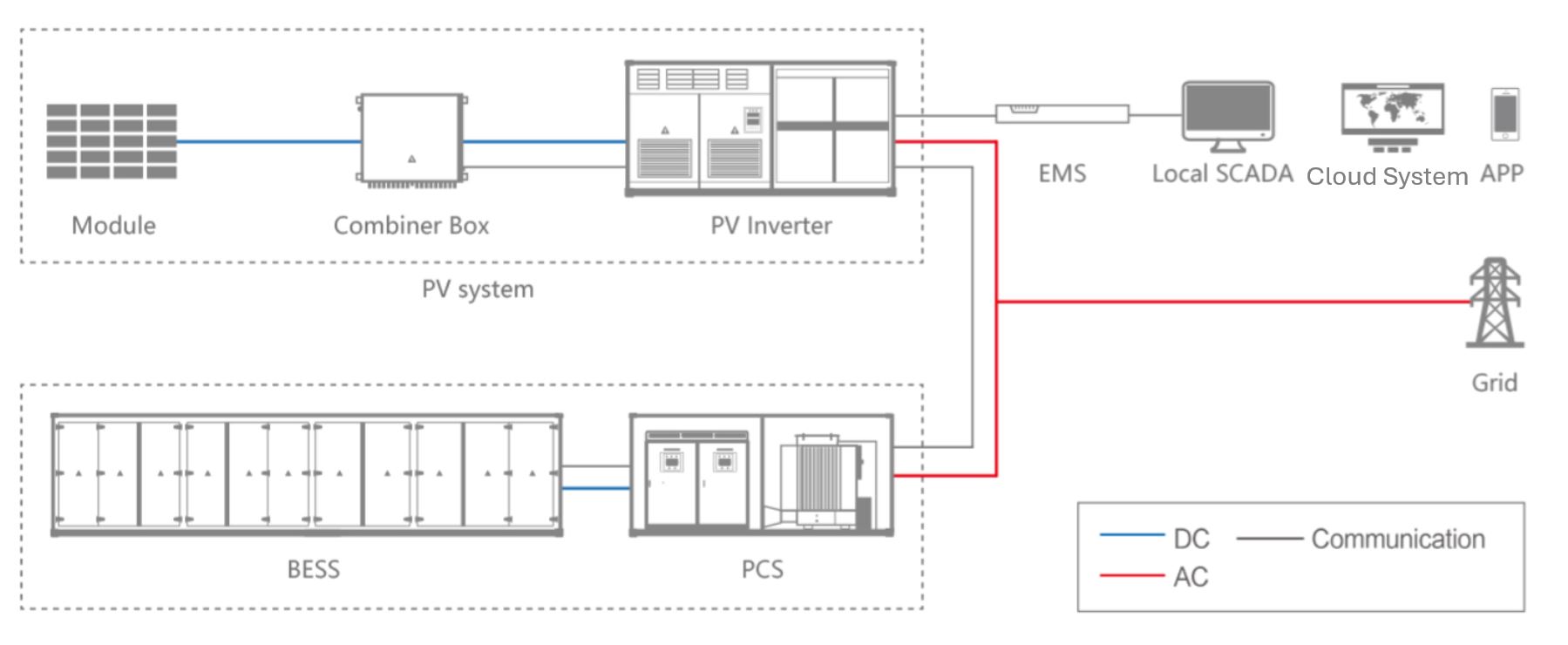
A BESS (Battery Energy Storage System) is a technology that stores electrical energy in large-scale batteries for later use, enhancing the stability and efficiency of power grids. It enables the integration of renewable energy sources like solar and wind by balancing supply and demand, providing peak shaving, frequency regulation, and backup power during outages. BESS systems typically consist of battery modules, inverters, thermal management, and control systems, and they are increasingly vital for modern energy infrastructure due to their ability to improve grid resilience, reduce reliance on fossil fuels, and support the transition to cleaner energy.
The key components of a BESS (Battery Energy Storage System) include battery modules or cells that store electrical energy, inverters that convert direct current (DC) from the batteries to alternating current (AC) for grid use, a battery management system (BMS) that monitors and manages battery health, thermal management systems to regulate temperature and ensure safety, power conversion systems for efficient energy transfer, and control systems that coordinate operation, safety mechanisms, and communication interfaces for seamless integration with the grid.
To operate and manage a BESS effectively, several software components are essential, including Battery Management System (BMS) software that monitors battery health and safety, energy management systems (EMS) for optimizing charge/discharge cycles, grid management software for integrating the BESS into the power grid, fault detection and diagnostic tools for maintenance, and SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) systems for real-time monitoring and control. Additionally, advanced analytics and forecasting software may be used to predict energy demand and optimize system performance, ensuring safe, efficient, and reliable operation of the BESS.
The technical risks of a BESS (Battery Energy Storage System) include potential thermal runaway leading to fires or explosions, degradation of battery capacity over time affecting performance, software malfunctions causing operational errors, hardware failures such as inverter or connection issues, and safety hazards related to high-voltage systems. Other risks involve cybersecurity threats to control systems, improper maintenance leading to reduced lifespan, and integration challenges with existing grid infrastructure. Proper design, regular maintenance, and advanced safety protocols are essential to mitigate these risks and ensure reliable, safe operation of the BESS.
Liquid-cooled BESS (Battery Energy Storage Systems) can help reduce fire risk compared to air-cooled systems by providing more effective thermal management, preventing overheating and thermal runaway, which are primary causes of battery fires. The liquid cooling system maintains consistent temperatures across the battery modules, reducing hot spots and controlling heat buildup that can lead to fires. However, it introduces additional safety considerations, such as the potential for leaks or chemical hazards associated with the cooling fluid. Overall, while liquid cooling enhances thermal safety and can lower fire risk, it must be properly designed, maintained, and monitored to ensure maximum safety benefits.
The commercial risks of a BESS (Battery Energy Storage System) include high capital and operational costs, which can impact profitability if energy prices or demand forecasts are inaccurate, as well as potential regulatory and policy changes that could affect market incentives or compliance requirements. Additionally, technological obsolescence, battery degradation over time, and warranty limitations pose financial risks, along with risks related to grid integration challenges and potential safety incidents that could lead to liability or insurance costs. Market volatility and competition from alternative energy solutions also influence the return on investment, making careful financial planning and risk management essential for commercial success.
Investing in a BESS (Battery Energy Storage System) makes sense due to its ability to enhance energy reliability, facilitate the integration of renewable sources, and generate revenue through services like peak shaving, frequency regulation, and energy arbitrage. As the global shift toward clean energy accelerates, BESS systems offer strategic advantages by stabilizing the grid, reducing operational costs, and providing backup power. Although initial capital costs and technological risks exist, the long-term benefits—including improved grid resilience, potential income streams, and alignment with sustainability goals—make BESS a compelling investment, especially with evolving regulations and increasing demand for renewable energy integration.
Development trends for BESS (Battery Energy Storage Systems) include advancements in battery chemistries such as solid-state and lithium-silicon batteries for higher energy density and safety, increased focus on grid-scale deployments to support renewable integration and grid stability, and the integration of smart, AI-driven management software for optimized performance and predictive maintenance. Additionally, there is a trend toward modular and scalable designs for easier deployment and upgrades, improved thermal management systems to enhance safety and longevity, and the adoption of second-life batteries to reduce costs and environmental impact. As policies and market demands evolve, BESS technology is also moving toward greater efficiency, cost reduction, and wider application in sectors like electric vehicles, microgrids, and industrial power management.
Yes, the EU has introduced new regulations focused on the sustainable recycling and lifecycle management of batteries, including BESS (Battery Energy Storage Systems), under the proposed EU Battery Regulation, which is expected to be fully implemented by 2027. These regulations aim to ensure that batteries, including large-scale BESS, are designed for easier recycling, contain recycled materials, and have clear sustainability and safety standards. They set ambitious targets for collection, recycling efficiency, and the use of recycled content, promoting a circular economy and reducing environmental impact. Compliance with these regulations will be mandatory for market access, emphasizing responsible sourcing, reuse, and recycling practices for BESS systems across the EU.